NTA NET PAPER 1 :- Common Computer Abbreviations
Operating
Systems and Data Storage Based
- BIOS – This is the Basic Input
Output System which controls the computer, telling it what operations to
perform. These instructions are on a chip that connects to the
motherboard.
- BYTE – A byte is a storage unit
for data.
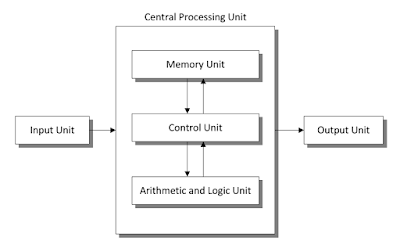
- CPU – This stands for the Central
Processing Unit of the computer. This is like the computer’s brain.
- OS – This is the Operating System
of the computer. It is the main program that runs on a computer and begins
automatically when the computer is turned on.
- PC – This is the abbreviation for
personal computer. It refers to computers that are IBM compatible.
- PDF – This represents the Portable
Document Format which displays files in a format that is ready for the
web.
- RAM – This stands for Random Access Memory which is the
space inside the computer that can be accessed at one time. If you
increase the amount of RAM, then you will increase the computer’s speed.
This is because more of a particular program is able to be loaded at one
time.
- ROM – This is Read Only Memory
which is the instruction for the computer and can not be altered.
- VGA – The Video Graphics Array is
a system for displaying graphics. It was developed by IBM.
- WYSIWYG – This initialism stands for
What You See Is What You Get. It is pronounced “wizziwig” and basically means that the printer will
print what you see on your monitor.
Internet Network Based
- FTP – This is a service called File Transport Protocol which moves a file between computers using the Internet.
- HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language formats information so it can be transported on the Internet.
- HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a set of instructions for the software that controls the movement of files on the Internet.
- IP – This stands for Internet Protocol which is the set of rules that govern the systems connected to the Internet. IP Address is a digital code specific to each computer that is hooked up to the Internet.
- ISP – The Internet Service Provider is the company which provides Internet service so you can connect your computer to the Internet.
- LAN – This stands for Local Area Network which is the servers that your computer connects to in your geographic area.
- PPP – Point-to-Point Protocol is the set of rules that allow your computer to use the Internet protocols using a phone line and modem.
- URL – This is the Uniform Resource Locator which is a path to a certain file on the World Wide Web.
- USB – The Universal Serial Bus is used for communications between certain devices. It can connect keyboards, cameras, printers, mice, flash drives, and other devices. Its use has expanded from personal computers to PDAs, smartphones, and video games, and is used as a power cord to connect devices to a wall outlet to charge them.
- VR – Virtual Reality simulates a three-dimensional scene on the computer and has the capability of interaction. This is widely used in gaming.
- • AGP –>Accelerated Graphic Port
- • PC –>Personal Computer
- • EPROM –>Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
- • BIOS –>Basic Input and Output System
- • HDD –>Hard Disk Drive
- • PCI –>Peripheral Component Interconnect
- • UNIVAC –>Universal Automatic Computer
- • GUI –>Graphic User Interface
- • USB –>Universal Serial Bus
- • VGA –>Visual Graphic Adaptor
- • MAN –>Metropolitan Area Network
- • ASCII –>American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- • WAN –>Wide Area Network
- • EBCDIC –>Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
- • LAN –>Local Area Network
- • EEPROM/EAPROM –>Electrical Erasable/Alterable Programmable Read Only Memory
- • CPU –>Central Processing Unit
- • OS –>Operating System
- • ALU –>Arithmetic and Logic Unit
- • DVD –>Digital Versatile Disc
- • CD –>Compact Disk
- • ROM –>Read Only Memory
- • VDU –>Visual Display Unit
- • RAM –>Random Access Memory
- • ICT –>Information Communication Technology
- • PROM –>Programmable Read Only Memory
- • URL –>Uniform Resource Locator
- • IDE –>Integrated Drive Electronics
- • FORTRAN –>Formular Translator
- • MOS –>Metaoxide Semi Conductor
- • ATX –>Advanced Technology Extended
- • SIM –>Subscriber Identification Module
- • MHZ –>Megahertz
- • ISP –>Internet Service Provider
- • GHZ –>Gigahertz
- • DBMS –>Database Management System
- • SQL –>Structured Query Language
- • RW –>Re-Writeable
- • SDT –>Serial Data Transmission
- • CAN –>Campus Area Network
- • SIMMs –>Single In-line Memory Module
- • PAN –>Personal Area Network
- • DIMMs –>Dual In-line Memory Module
- • CMOS –>Complimentary Metaoxide Semi Conductor
- • ENIAC –>Electronic Number Integrator And Calculator
- • CMD –>Command
- • EDSAC –>Electronic Dialog Storage Automatic Computer
- • MAC –>Media Access Control
- • IC –>Integrated Circuit
- • LSIC –>Large Scale Integrated Circuit
- • DIR –>Directory
- • GIGO –>Gabbage In Gabbage Out
- • PHP –>PHP Hypertext Preprocessor
- • DOC –>Document
- • PDT –>Parallel Data Transmission
- • PDA –>Personal Digital Assistant
- • USSD –>Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
- • WWW –>World Wide Web
- • COBOL –>Common Basic Oriented Language
- • CCNP –>Cisco Certified Network Professionals
- • BASIC –>Beginner All Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code
- • CEH –>Certified Ethical Hacking
- • TCP –>Transmission Control Protocol
- • CSS –>Cascading Style Sheet
- • CISCO –>Computer Information System Company
- • XXS –>Cross Site Scripting
- • XML –>Extensible Mark-up Language
- • HTML –>Hypertext Markup Language
- • CCNA –>Cisco Certified Network Associate
- • RFI –>Remote File Inclusion
- • HTTP –>Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- • DDOS –>Distribution Denial Of Service
- • VPN –>Virtual Private Network
- • SEO –>Search Engine Optimization
- • IP –>Internet Protocol
The most common document file extensions are:
- .DOC and DOCX
- .HTML and .HTM
- .XLS and XLSX
- .PPT and .PPTX
- .TXT
- .jpg
- .png
Funamentals of Computer
ICT and Governance
The “e” in e-Governance stands for ‘electronic’. Thus, e-Governance is basically associated with carrying out the functions and achieving the results of governance through the utilization of ICT (Information and Communications Technology).
In this century where almost everything has been made electronic like e-commerce, e-service, e- learning, etc. the Indian government is also trying to go with the wave and wants to govern through ICT. E-governance needs the help of ICT services to achieve their objective anytime and anywhere. It eliminates the need of physical travel by citizens to various government offices in order to get their work done.
The major objective of e-governance is to support and simplify governance for all the government agents, citizens and businesses.
E-governance also means e-democracy where all forms of communications between the electorate and the electoral happen electronically or digitally.
Background
India is country of villages and for overall prosperity, growth and sustainable development ,ICT and Governance play a key role not only in terms of e-Governance models to demonstrate the key changes we see in the services for healthcare, education, banking, mobility, agriculture and other allied fields but also to keep country on the path of development in emerging competition on various fronts from other countries.
1970 : Department of Electronics
1977 : National Informatics Centre(NIC)
1980 : Use of computers began
1987 : Launch of NICENET & DISNIC
1998 : National Task Force on Information Technology and Software Development 1999 : Union Ministry of Information Technology
2000 -05: 12 point e-Governance launched by central & state Govt with focus on G2C,G2B, G2G initiatives
2006 -11: National e-Government Plan(NeGP) 2012 -17: Current E-GoV & Digital India
ICT and Governance
The term e-governance focuses on the use of new ICT by governments as applied to the full range of government functions. Thus e-governance is the application of information and communication technology for delivering government services, exchange of information, communication, transaction, integration, various stands alone systems and services between government and citizens, government and business as well as back office process and interaction within the entire government frame work.
ICT acts in speeding up the flow of information and knowledge between government and citizen and transforming the way in which government and citizen interact.
Types of Government Interaction in e-governance.
G2G:
Government to Government
G2C:
Government to Citizen
G2B: Government to Business
G2E:
Government to Employee
Benefits
Increases accountabilityIncreases transparency
Higher availability of public domain information
Reduces corruption
Higher penetration due to automation
Increases efficiency due to connectivity
2006 -11: National e-Government Plan(NeGP)
National e-Governance Plan(NeGP) – make all government services accessible to common man in his locality, through common service delivery outlets and ensure efficiency, transparency & reliability of such services at affordable cost to realize the basic needs of the common man.
Initiatives under NeGP
State Wide Area Networks – connect all state
State Data Centres – host Govt apps
Common Services Centres – internet enabled centres at district level
Electronic forms through state portal – download forms & submit applications
Capacity Building – implementation from city to village
E-District – provide district administration services by web services like right to information, social welfare, ration card, birth & death certificate etc.
Citizen engagement – deep awareness of project
Current E-Gov – 12th 5yr plan (2012-17)
Deliver all Govt services in electronic mode so as to make Govt process transparent, citizen centric, efficient and easy accessible
Create
sharable resources for all Govt entities
To
deliver both information & transaction of Govt services over mobile
Build shared service platforms to accelerate e-Gov project implementation
To strengthen & improve existing project through innovation and infusion of advanced technology
To promote ethical use of technology & data and create safe & secure cyber world
To create ecosystem that promotes innovation in ICT for governance & for applications that can benefit the citizens Ø To better target welfare schemes of central & state Govt
To increase all round awareness & create mechanism that promotes & encourages citizen engagement
To make available as much data as possible in public domain for productive use by citizens
Build shared service platforms to accelerate e-Gov project implementation
To strengthen & improve existing project through innovation and infusion of advanced technology
To promote ethical use of technology & data and create safe & secure cyber world
To create ecosystem that promotes innovation in ICT for governance & for applications that can benefit the citizens Ø To better target welfare schemes of central & state Govt
To increase all round awareness & create mechanism that promotes & encourages citizen engagement
To make available as much data as possible in public domain for productive use by citizens
Digital
India
The
Digital India programme is a flagship programme of the Government of India with
a vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge
economy.
The
focus is on being transformative – to realize IT + IT = IT The focus is on
making technology central to enable change. It is an Umbrella Programme –
covering many departments.
It
weaves together a large number of ideas and thoughts into a single,
comprehensive vision so that each of them is seen as part of a larger goal.
1.
Each individual element stands on its own. But is also part of the larger
picture.
2.
It is coordinated by DeitY, implemented by the entire government.
3. The weaving together makes the Mission transformative in totality
3. The weaving together makes the Mission transformative in totality
The Programme:
1.
Pulls together many existing schemes.
2. These schemes will be restructured and re-focused.
3. They will be implemented in a synchronized manner.
4. Many elements are only process improvements with minimal cost.
5. The common branding of programs as Digital India highlights their transformative impact.
2. These schemes will be restructured and re-focused.
3. They will be implemented in a synchronized manner.
4. Many elements are only process improvements with minimal cost.
5. The common branding of programs as Digital India highlights their transformative impact.
Nine
Pillars of Digital India
- Broadband highways – To support
Broadband for all Rural, Broadband for all Urban & National
Information infrastructure by DoT & DeitY
- Universal access to mobile
connectivity- For providing coverage to uncovered villages with mobile
connectivity
- Public internet access programme-
This has two important sub components
1. CSCs- Aims to cover each gram panchayat to provide delivery of e_services to the citizens 2. Post-Office- To be converted into multi service centers - E-governance – reforming
government through technology
- Online applications and tracking – Online applications and tracking of their status should be provided.
- Online repositories – Use of online repositories e.g. for certificates, educational degrees, identity documents, etc. should be mandated so that citizens are not required to submit these documents in physical form.
- Integration of services and platforms – Integration of services and platforms e.g. Aadhaar platform of Unique Identity Authority of India (UIDAI), payment gateway, Mobile Seva platform, sharing of data through open Application Programming Interfaces (API) and middleware such as National and State Service Delivery Gateways (NSDG/SSDG) should be mandated to facilitate integrated and interoperable service delivery to citizens and businesses.
- Ekranti – electronic delivery of
services- There are 44 Mission Mode Projects under e-Kranti programme.
These mission mode projects are grouped into Central, State and Integrated
projects.
- Information for all- Open Data
platform, Social Media Engagement and Online Messaging
- Electronics manufacturing-
promoting electronics manufacturing in the country with the target of NET
ZERO Import by 2020
- IT for jobs- This pillar focuses
on providing training to the youth in the skills required for availing
employment opportunities in the IT/ITES sector.
- Early harvest programmes- Early
Harvest Programme basically consists of those projects which are to be implemented
within short timeline. Such as Biometric attendance, Wi-Fi in public
places, secure email, SMS based alerts.
Key
Points to remember
The
National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) has been formulated by the Department of
Electronics and Information Technology (DEITY) and Department of Administrative
Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) in 2006.
Comments
Post a Comment